Understanding Spark Plug Part Numbers
Back in the days when a 350hp 308 was an incredible achievement and no-one had even considered 600 pump fuel horsepower, spark plug selection was pretty much a ‘go with what you know’ situation. But these days, we’re making more power than ever before and with that extra mumbo comes extra heat and the need to be all the more accurate with both parts and fuel selection. Sure, the quality and durability of engine parts has improved dramatically in the last twenty years but the more resources that are made available to engine builders in the form of lighter, stronger components, the further they want to push the envelope. And the harder they push, especially on pump fuel, the smaller the margin for error becomes.
This is where correct spark plug selection plays an important role with a poor choice usually resulting in a reduction in horsepower and torque but sometimes ending up in disaster.
If you pick up any spark plug catalogue these days, you’ll see something that resembles the phone book rather than a simple parts listing.
For such a small, consumable part of the engine, someone has sure put a lot of effort into confusing the average car guy with enough part numbers to send us all ‘round the bend. There is method in the manufacturers’ madness though and with a copy of the key a particular manufacturer might use, you’ll soon be reading plug part numbers as easily as you’d decipher the weight of your favourite engine oil.
Unfortunately, there doesn’t seem to be a universal naming system for spark plugs so instead you have to rely on the information made available by the manufacturer of a plug. If all you ever buy is NGK then you’ll get used to how they do things. If you’re a Bosch fan then you’ll need to get a handle on their codes. Most manufacturers make this information readily accessible on their websites as well as in their catalogues.
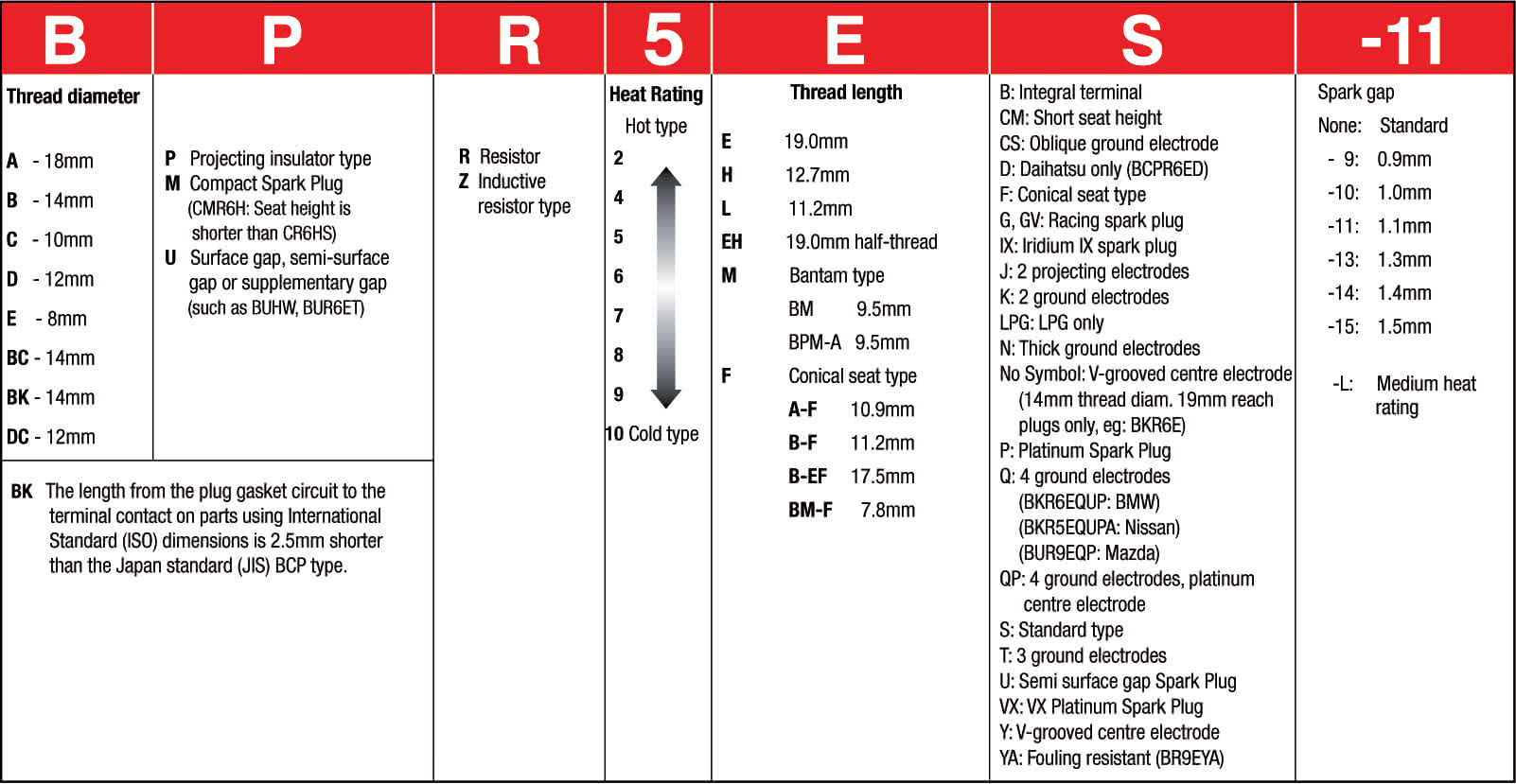
BCPR5ES-11 VS. WR8AC
Let’s have a look at a fairly common plug from NGK and a Bosch plug for a VW Beetle. Breaking it down into its components makes understanding the makeup of this plug easy provided you have the key.
Remember that for this example, the higher the heat rating for the NGK, the ‘colder’ the plug is. The opposite is true for the Bosch plug.
BCPR5ES-11
- BC – Thread diameter is 14mm
- P – Projecting insulator type
- R – Resistor
- 5 – Heat rating of 5
- E – Thread length is 19.0mm
- S – Standard type
- 11 – Plug gap is 1.1mm
WR8AC
- W – Thread is 14mm x 1.25
- R – With suppression resistor
- 8 – Heat rating is 8
- A – Thread length is 12.7mm
- C – Electrode material is Copper
Now that you understand how to decode spark plug numbers and select the right ones for your engine, it’s time to put that knowledge into action. We have another handy DIY on how to replace spark plugs which guides you through the step-by-step process of replacing your spark plugs, from gathering the right tools to ensuring a perfect fit. Alternatively, if you'd like to start with the basics, we recommend exploring our spark plugs 101 guide to learn more about what spark plugs do.
*Important information* - Click here to read more about our DIY Advice Terms and Conditions.